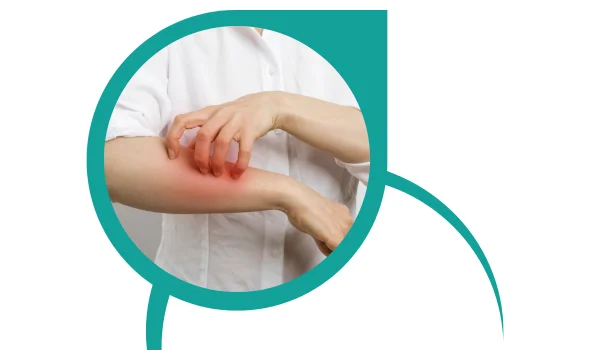
What are Allergies?
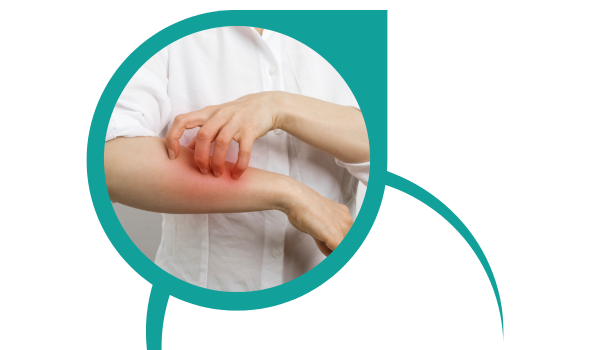
Allergies are an immune system response to substances known as allergens. These allergens can be harmless, everyday substances such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, or insect venom. When a person with allergies comes into contact with an allergen, their immune system overreacts, releasing chemicals that cause symptoms. These symptoms can range from mild, such as sneezing and itching, to severe, such as difficulty breathing and anaphylaxis. Allergies can develop at any age, and while there is no cure, management involves avoiding allergens, taking medications, and undergoing immunotherapy to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Allergies Symptoms:
Allergy symptoms can vary but commonly include sneezing, itching, runny nose, nasal congestion, watery eyes, coughing, wheezing, hives, swelling, itching or tingling sensations, shortness of breath, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
Symptoms due to Food Allergies:

Food allergies can cause a range of symptoms, which can appear within minutes to hours after consuming the allergenic food. Common symptoms include hives, itching, swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, dizziness, or even anaphylaxis. Skin reactions like eczema or itchy rashes can also occur. It’s important to note that food intolerances, which do not involve the immune system, can cause similar symptoms but are not classified as allergies. If you suspect a food allergy, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.


Symptoms due to Seasonal Allergies:

Seasonal allergies, also known as hay fever or allergic rhinitis, can cause a variety of symptoms. These typically occur when an individual is exposed to specific allergens like pollen from trees, grasses, or weeds. Symptoms include sneezing, itching, a runny or stuffy nose, watery or itchy eyes, coughing, and fatigue. Some people may also experience a sore throat, headaches, or sinus pressure. The severity of symptoms can vary, but they commonly occur during specific times of the year when particular allergens are prevalent. Appropriate management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve daily functioning during allergy seasons.
Severe Allergies:
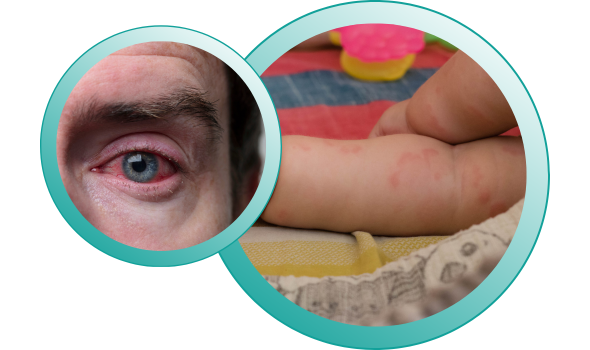
Severe allergies, also known as anaphylaxis, are potentially life-threatening allergic reactions. They can occur within seconds or minutes after exposure to an allergen, such as certain foods, insect venom, medications, or latex. Symptoms of severe allergies can include difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, hives, rapid pulse, dizziness, fainting, nausea, and abdominal pain. Anaphylaxis requires immediate medical attention, and individuals at risk are often prescribed epinephrine auto-injectors to be used in case of an emergency. Prompt recognition, avoidance of triggers, and emergency preparedness are crucial for managing severe allergies.
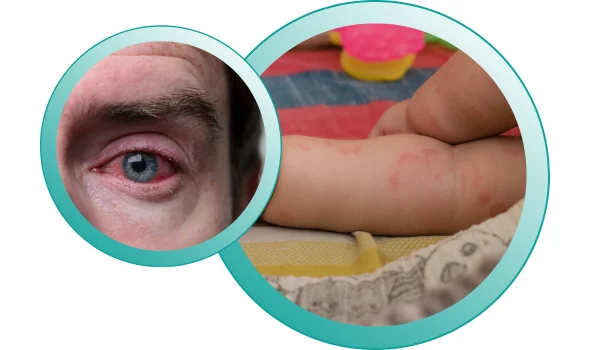
Asthma and Allergies:
Asthma and allergies often have a strong connection, as allergies can be a significant trigger for asthma symptoms. Allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold spores can cause an allergic reaction in susceptible individuals, leading to inflammation and narrowing of the airways in the lungs. This allergic response can result in asthma symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
Managing asthma and allergies involves a comprehensive approach. It includes identifying and avoiding allergens, using medications to control both conditions, and creating an asthma action plan. This plan may include the use of inhalers, oral medications, or allergy shots (immunotherapy) to alleviate symptoms and prevent asthma attacks triggered by allergies. Regular communication with healthcare professionals is vital for proper diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management of asthma and allergies to achieve optimal control and improve the overall quality of life.
Skin Allergies:
Skin allergies, also known as allergic dermatitis, occur when the skin reacts to certain substances or allergens. Common triggers include chemicals, cosmetics, certain metals (such as nickel), medications, plants like poison ivy, and even certain fabrics. When the skin comes into contact with these allergens, it may develop symptoms like redness, itching, swelling, rashes, or blisters. Skin allergies can be acute or chronic, and the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person. Treatment often involves avoiding the allergen, using over-the-counter or prescription topical creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and itching, and taking antihistamines to alleviate symptoms. In some cases, a doctor may recommend allergy testing or immunotherapy for long-term management. Regular skincare routines and gentle care of the affected areas can help prevent flare-ups and maintain healthy skin.

The common types of skin allergies are:

The common types of skin allergies include contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis (eczema), hives (urticaria), and angioedema. Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with an allergen or irritant. Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Hives are raised, itchy welts that can appear suddenly and disappear within hours. Angioedema involves deep swelling in the layers of the skin, often affecting the face and lips. These types of skin allergies can cause discomfort and require appropriate diagnosis and management by healthcare professionals.
Causes of Allergies:
Allergies can be caused by various factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental exposure to allergens, and an overactive immune system. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, insect venom, medications, and latex. Understanding the specific triggers is crucial for managing and avoiding allergic reactions.
The common types of allergens are:
The common types of allergens are diverse and can be found in various environments. Outdoor allergens include pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds, as well as mold spores. Indoor allergens include dust mites, pet dander, cockroach droppings, and mold. Certain foods like peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, eggs, milk, and wheat can also trigger allergies. Other allergens include insect venom from bee stings or mosquito bites, certain medications like penicillin, latex, and even certain metals such as nickel. Identifying and avoiding exposure to these allergens is crucial for individuals prone to allergies to minimize symptoms and allergic reactions.
Allergy Diagnosis:
Diagnosing allergies typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. It begins with obtaining a detailed medical history, including a discussion of symptoms and potential triggers. A physical examination may be performed to assess any visible signs of allergic reactions. Allergy testing plays a significant role in diagnosis and may include skin prick tests or blood tests, such as specific IgE antibody tests, to identify allergens causing the allergic response. These tests help determine the specific substances an individual is allergic to and the severity of their allergies. In some cases, an oral food challenge or an elimination diet may be conducted to assess food allergies. The information gathered through these diagnostic methods enables healthcare providers to develop personalized management plans and recommend appropriate treatment options for individuals with allergies.
Allergy Treatments:
Allergy treatments aim to alleviate symptoms, manage allergic reactions, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with allergies. The primary approach involves avoiding exposure to known allergens whenever possible. Medications, such as antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, decongestants, or eye drops, may be prescribed to relieve symptoms like sneezing, itching, congestion, or redness. For severe allergies or anaphylaxis, epinephrine auto-injectors are used as emergency treatment. Allergen immunotherapy, commonly known as allergy shots, may be recommended for long-term management. This treatment involves gradually exposing the body to increasing amounts of allergens to build tolerance and reduce allergic reactions. It is essential for individuals with allergies to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment options for their specific allergies and symptoms.
The other therapies in the treatment are:
Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots, is a treatment option for allergies. It involves regular injections of small amounts of allergens over time, aiming to desensitize the immune system. The goal is to reduce the severity of allergic reactions and symptoms by gradually increasing tolerance to specific allergens.
Emergency epinephrine:
Emergency epinephrine, commonly administered through auto-injectors like EpiPen, is a life-saving treatment for severe allergic reactions or anaphylaxis. Epinephrine works by rapidly constricting blood vessels, relaxing airway muscles, and reducing immune response. It is crucial for individuals with severe allergies to carry and use epinephrine in case of an emergency to counteract severe allergic reactions and prevent further complications.
Quick Contact
Address
70, 46, Patel Marg, opposite Rastogi Gas Agency, Mansarovar Sector 7, Agarwal Farm, Sector 9, Mansarovar, Jaipur, Rajasthan 302020
deveshkanoongo0701@gmail.com
Phone No.
9024605799, 9414774975
