
What is Asthma disease?

Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to recurring episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing. It affects people of all ages, but often starts in childhood. Asthma can be triggered by various factors such as allergens (pollen, dust mites), irritants (smoke, pollution), exercise, and respiratory infections. During an asthma attack, the muscles surrounding the airways tighten, and the lining of the air passages becomes swollen, causing the airways to narrow, making it difficult for air to move in and out of the lungs. Asthma is manageable with proper diagnosis, medication, and avoidance of triggers.
Asthma Types
There are four major types of asthma

Mild intermittent
Asthma
Mild intermittent asthma refers to a form of asthma where symptoms occur infrequently, typically less than twice a week, and do not interfere with daily activities.
Mild Persistent
Asthma
Mild persistent asthma refers to a form of asthma where symptoms occur more than twice a week but less than once a day, and may slightly affect daily activities.

Moderate Persistent Asthma
Moderate persistent asthma refers to a form of asthma where symptoms occur daily, affect daily activities, and may require daily medication to control inflammation and prevent exacerbations.
Severe Persistent
Asthma
Severe Persistent Asthma is a chronic and debilitating lung condition with persistent and severe symptoms that necessitate intensive treatment and management strategies.
Asthma Causes:
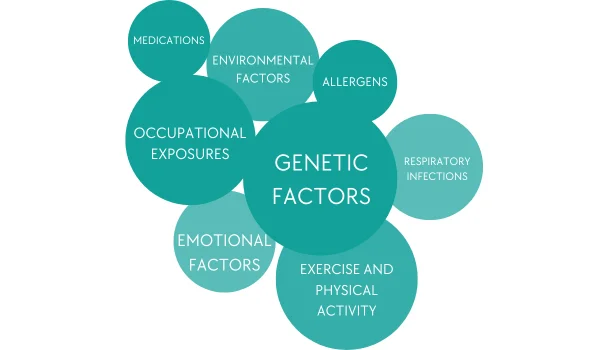
The exact causes of asthma are not fully understood, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to play a role. Individuals with a family history of asthma are more likely to develop the condition. Exposure to certain allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold, can trigger asthma symptoms in susceptible individuals. Irritants like smoke, air pollution, strong odors, and chemicals can also exacerbate symptoms. Respiratory infections, especially during early childhood, can contribute to the development of asthma. Additionally, certain factors like obesity, exposure to secondhand smoke, and occupational exposure to certain substances (e.g., chemicals, dust, or fumes) can increase the risk of developing asthma. Hormonal changes, emotional stress, and physical activity can also trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals. It is important to identify and avoid triggers to effectively manage asthma symptoms.


Diagnosis of Asthma

The diagnosis of asthma involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The doctor will inquire about symptoms, their frequency and triggers, as well as family history of asthma or allergies. A physical examination may reveal signs such as wheezing or a prolonged expiratory phase. To confirm the diagnosis, lung function tests are conducted, including spirometry, which measures how much air a person can exhale forcefully, and a bronchodilator test, which assesses the response to a medication that opens up the airways. Allergy tests may also be performed to identify specific triggers. In some cases, additional tests like chest X-rays or sputum analysis may be recommended to rule out other conditions. It is crucial to obtain an accurate diagnosis to determine the severity of asthma and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Regular follow-up visits and monitoring of lung function are essential to assess asthma control and adjust medication as needed.
Asthma Treatment
Asthma treatment aims to control symptoms, prevent exacerbations, and improve the quality of life for individuals with asthma. The treatment plan is personalized based on the severity of the condition and the individual’s specific needs.
The primary approach involves using medications. Quick-relief medications, such as short-acting beta-agonists, provide immediate relief during asthma attacks by relaxing the muscles around the airways. Controller medications, such as inhaled corticosteroids, are used daily to reduce airway inflammation and prevent symptoms. Other long-acting bronchodilators, leukotriene modifiers, and oral corticosteroids may also be prescribed depending on the severity of asthma.
In addition to medications, avoiding triggers is essential. This may involve minimizing exposure to allergens like pollen or pet dander, reducing exposure to irritants like smoke or chemicals, and maintaining good indoor air quality. It is also crucial to have an asthma action plan, which outlines how to manage symptoms, adjust medication, and when to seek medical help.
Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is important to monitor asthma control, adjust treatment as needed, and address any concerns. Asthma education is also beneficial to ensure individuals understand their condition, medications, and proper inhaler techniques.
For severe and uncontrolled asthma, specialized treatments like biologic therapies may be considered. These targeted medications work on specific immune pathways to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms.
Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing comorbid conditions like allergies or acid reflux, can also contribute to better asthma control.
By following an individualized treatment plan, managing triggers, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with asthma can lead active and fulfilling lives with minimal symptoms and reduced risk of exacerbations.
Asthma Prevention
While asthma cannot be completely prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing asthma and minimize asthma symptoms.
- Avoiding triggers: Identify and avoid allergens or irritants that can trigger asthma symptoms, such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, smoke, and strong odors.
- Maintain good indoor air quality: Keep the home clean, well-ventilated, and free from dust, mold, and other potential allergens. Use air filters and regularly change them.
- Practice good hygiene: Wash hands regularly to reduce the risk of respiratory infections that can worsen asthma symptoms.
- Vaccinations: Stay up to date with vaccinations, including the flu vaccine, to prevent respiratory infections.
- Manage allergies: If you have allergies, work with a healthcare provider to develop an appropriate management plan to reduce allergic triggers.
- Avoid tobacco smoke: Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can worsen asthma symptoms and increase the risk of developing asthma.
- Regular exercise: Stay physically active, as regular exercise can help improve lung function and overall respiratory health.
- Follow a healthy lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, manage stress, and get enough sleep to support overall health and immune function.
While prevention measures can help reduce the likelihood of developing asthma or experiencing severe symptoms, it’s important to remember that asthma is a complex condition influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. If you suspect you have asthma or are at risk, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance.
Quick Contact
Address
70, 46, Patel Marg, opposite Rastogi Gas Agency, Mansarovar Sector 7, Agarwal Farm, Sector 9, Mansarovar, Jaipur, Rajasthan 302020
deveshkanoongo0701@gmail.com
Phone No.
9024605799, 9414774975
